Execution Context ( ⊃ Hoisting 개념 )
Execution Context(실행 컨텍스트)는 코드를 실행할떄 필요한 환경 정보들을 담은 객체이다.
동일한 환경에 있는 코드들을 실행할떄, 필요한 환경 정보들을 모아 context를 구성하고, 이를 call stack에 올렸다가, 가장 위에 쌓여있는 context와 관련있는 코드들을 실행하는 식으로 전체 코드의 환경과 순서를 보장한다.
(stack 자료구조에서 LIFO 을 생각하면 이해가 간편한다.)execution context 는 함수를 실행할떄 구성된다.
+) ES6 부터는 let,const block scope가 추가되었다.
여기서 call stack이란,
현재 어떤 함수가 동작하고 있는지와 다음에 어떤 함수가 호출되어야 하는지를 제어하는 자료구조이다.
코드 예시를 들면 다음과 같다.
1 | var a = 1; |
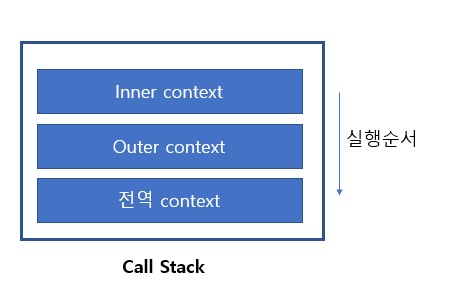
위의 코드에서 call stack은 다음과 같이 형성된다. javascript engine이 코드(함수)를 실행할떄 해당 환경에 대한 정보를 수집하여서 execution context를 만들고 call stack에 담는 형태이다.
그렇다면 정확히 어떤 환경에 대한 정보들을 수집하여 call stack 에 담기게 되는 것일까?
VariableEnvironment (environmentRecord 객체, outerEnvironmentReference 객체)
LexicalEnvironment (environmentRecord 객체, outerEnvironmentReference 객체 )
ThisBinding
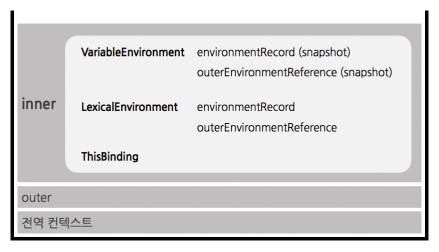
Variable Environment
책에 사진을 보면 LexicalEnvironment와 VariableEnvironment의 구성성분은 같아보이지만, 큰 차이점이 하나 있다.
VariableEnvironment는 최초 실행 시의 snapshot을 유지한다. 이후에 값이 변경되는 것은 LexicalEnvironment 에서 follow-up한다.
Lexical Environment
environmentRecord
Lexical Environment의 environmentRecord에는 현재 context의 식별자 정보를 담는다. 이떄 현재 context의 식별자 정보를 담을떄, 이를 간편하게 hoisting 이라고 한다.
정리를 하면 hoisting이란 식별자 정보를 실행 context의 맨 상단으로 끌어올리는 과정이다.
1 | // before hoisting |
1 | // after hoisting (예시 코드) |
처음 실행 context가 생성되는 순간에, environmentRecord의 정보가 수집된다. ( 정확히는 hoisting 과는 다르겠지만, hoisting 으로 이해하여도 결과는 동일하다. )
outerEnvironmentReference
outerEnvironmentReference 는 현재 execution context의 외부 식별자 정보를 담는다.
예를 들면 inner context에서 outerEnvironmentReference는 outer의 Lexical Environment 를 가르키고, outer context에서 outerEnvironmentReference는 전역 context를 가르킨다.
outerEnvironmentReference는 scope(변수의 유효범위) chain 현상을 유도한다.
즉 inner context에서는 environmentRecord를 통해 inner context에서 식별자를 접근할 수 있고, outerEnvironmentReference를 통해 외부 outer context 식별자도 접근이 가능하다.
이때 주의할 점은 scope chain 구조적 특성에 따라, 여러 scope에서 동일한 식별자를 선언한 경우에는 무조건 scope chain상에서 가장 먼저 발견된 식별자에만 접근이 가능하다는 점이다.
1 | var a = 1; |
반면 outer에서 inner context를 접근할 수는 없다.
1 | var a = 1; |
정리를 하면 , execution context 가 변수의 유효범위 scope를 정의한다.
Reference
- 정재남 - 코어 자바스크립트 (http://www.yes24.com/Product/Goods/78586788)