Item31. 한정적 와일드카드를 사용해 API 유연성을 높이라
Generic 타입 불공변 특성으로 인한 제약
1 | public class Stack<E> { |
Generic type Stack에서 pushAll method를 추가한다고 가정하자
Integer는 Number의 하위 타입임으로 아래의 method도 논리적으로는 정상작동해야 올바르지만, Generic의 불변성때문에 허용되지않고 compile error 가 나온다.
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
bounded wildcard type을 통한 유연성 제공
1 | // bounded wildcard type |
한정적 와일드카드 타입 ( bounded wildcard type ) 을 통해 불공변 특성을 가진 Generic 의 유연성을 높일수 있다.
PECS - producer-extends , consumer-super 공식
- 와일드카드 타입을 사용하는 기본 원칙으로, 매개변수화 타입 T가 생성자라면 <? extends T> 를 사용하고 , 소비자라면 <? super T> 를 사용하라는 공식이다.
위 Generic stack의 예에 적용해보면 다음과 같다.
pushAll의 매개변수인 Iterable은 값을 꺼내서(생성해주어서) stack에게 전달해주는 매개변수이다.
따라서 생성자라고 볼 수 있다. –> <? extends T> 를 사용한다.
1 | // PECS 공식 - 생성자 |
또 다른 stack의 method로 stack의 모든 원소를 차례로 꺼내서 매개변수에게 전달해주는 popAll() method를 예시로 들었다.
마찬가지로 generic은 불공변임으로 모든 객체의 부모class인 Object class임에도 불구하고 in-compatible type compile error 가 뜬다.
1 | Stack<Number> numberStack = new Stack<Number>(); |
PECS 공식을 적용해서 Collection<E> dst 매개변수를 보면 stack의 원소들을 전달받는(stack의 원소를 소비해서) 매개변수이다.
따라서 다음과 같이 수정해야한다.
또 다른 예제로 collection에서 max값을 찾아주는 max method에 한정적 와일드카드 타입을 적용하면 다음과 같다.
1 | public static <E extends Comparable<? super E>> E max(Collection<? extends E> c){ |
parameter는 collection에서 값을 생성해줌으로 extends , 반환타입인 comparable은 값을 소비함으로 super 를 적용하였다
- Comparable은 언제나 소비자임으로, 일반적으로 Comparable<E>보다는 Comparable<? super E> 를 사용하는 편이 낫다.
꼭 PECS 공식을 적용해서 코드를 복잡하게 만들어야 하는 이유가 있을까?
구체적인 예를 보면 아래의 list는 PECS 규칙을 적용한 max method에만 적용된다.
1 | public interface Comparable<E> |
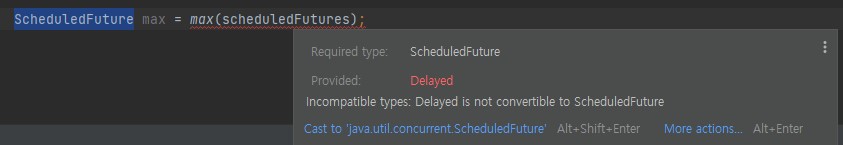
ScheduledFuture는 Comparable을 상속받은 Delayed Interface를 상속받았다.
max method의 반환타입인 E extends Comparable<E> 를 보면 Comparable<ScheduledFuture> type은 존재할 수 없기 때문이다.
유의점
반환타입에서는 한정적 와일드카드타입을 사용하면 client에서도 한정적 와일드카드 타입을 써야함으로 반환타입에는 사용하면 안된다.
compiler 가 올바른 타입을 추론하지 못할떄는 명시적 타입 인수를 사용해서 타입을 알려주면 된다. 이는 JDK 8부터는 Target typing을 지원하지만 JDK 7까지는 발생할 수 있는 문제이다.
Target typing (Type Inference , Generalized Target-Type Inference ) : 타입 추론으로 말 그대로 compiler 가 타입을 추론해서 불필요한 boilerplate 코드를 줄여준다.
(https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se8/html/jls-18.html)
1 | // type inference 도입 전 |
타입 매개변수와 wildcard간 선택
1 | public static <E> void swap(List<E> list,int i ,int j) // 타입매개변수 사용 |
generic을 활용해 method 선언시 wildcard와 타입매개변수중 어떤것을 사용해야 할까?
- method 선언에 타입 매개변수가 한번만 나오면 wild card로 대체하는 것을 권고한다.
위 예제는 하나의 매개변수만 나옴으로, wildcard를 선택하였으나, wildcard collection은 null이외의 값을 넣을 수 없다.
책에서는 해결방안으로 wildcard 의 실제 타입을 알려주는 private 도우미 method를 활용하라고 제시하고 있다.
1 | public static void swap(List<?> list,int i ,int j){ |
정리
generic type에 wildcard type을 PECS 규칙을 사용해 적용하면 generic의 장점과 generic의 불공변 제약으로 부터 유연함을 동시에 취할 수 있다.